Grade B and Grade C are two different grades under the ASTM A500 standard.
ASTM A500 is a standard developed by ASTM International for cold formed welded and seamless carbon steel structural tubing.
Next, let's compare and contrast them in a variety of ways to understand what similarities and differences they have.

Differences
ASTM A500 Grade B and C differ significantly in chemical composition, tensile properties, and application areas.
Differences in Chemical Composition
In the ASTM A500 standard, there are two methods of analysis for the chemical composition of steel: thermal analysis and product analysis.
Thermal analysis is performed during the melting process of the steel. Its purpose is to ensure that the chemical composition of the steel meets the requirements of a specific standard.
Product analysis, on the other hand, is performed after the steel has already been made into a product. This method of analysis is used to verify that the chemical composition of the final product meets the specified requirements.
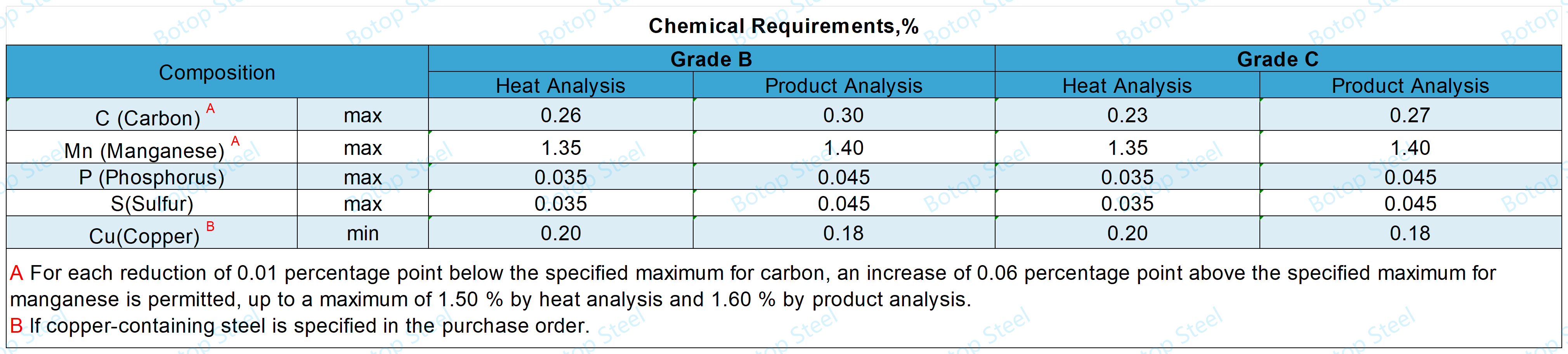
Not surprisingly, the carbon content of Grade C is slightly lower than that of Grade B, which may mean that Grade C has better toughness when welding and molding.
Differences in Tensile Properties
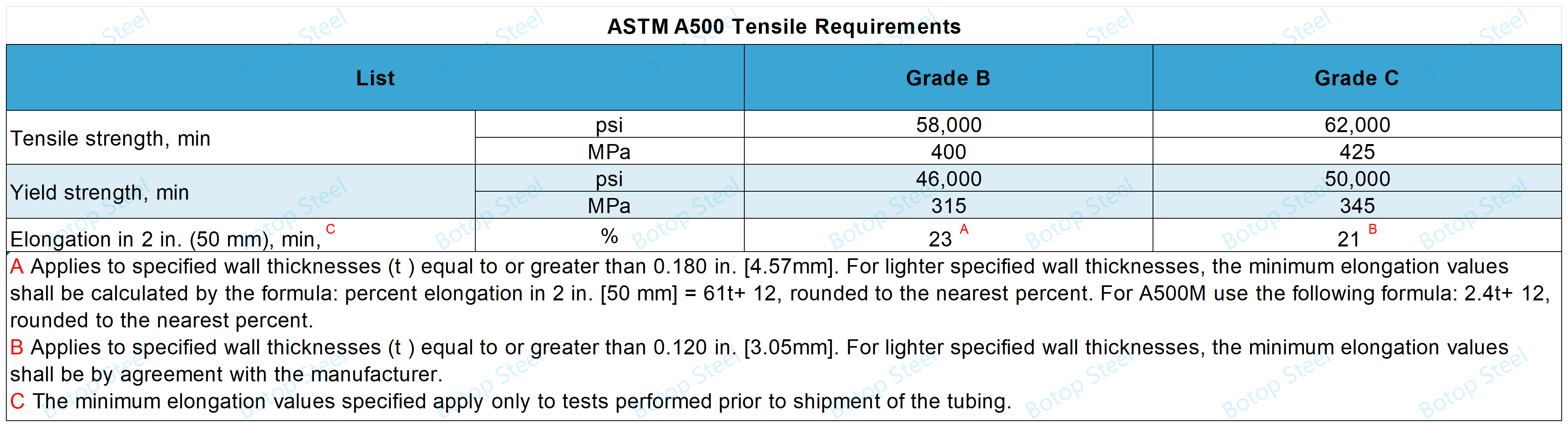
Grade B: Typically has a high degree of ductility, allowing it to extend in tension without breaking, and is suitable for structures that require some bending or deformation.
Grade C: Has higher tensile and yield strengths due to its chemical composition, but may be slightly less ductile than Grade B.
Differences in Application
Although both are used in structural and support applications, the emphasis is different.
Grade B: Due to its better welding and forming properties, it is often used in building structures, bridge construction, building supports, etc., especially when structures need to be welded and bent.
Grade C: Due to its higher strength, it is often used in applications that are subject to higher loads, such as industrial construction, heavy machinery support structures, and so on.
Commonality
While Grade B and Grade C differ in several ways, they also share common characteristics.
Same Cross-section Shape
Hollow section shapes are round, square, rectangular, and oval.
Heat Treatment
All allow the steel to be stress-relieved or annealed.
Same Test Programs
Both Grade B and C are required to meet the requirements of ASTM A500 for thermal analysis, product analysis, tensile testing, Flattening Test, Flaring Test, and Wedge Crush Test.
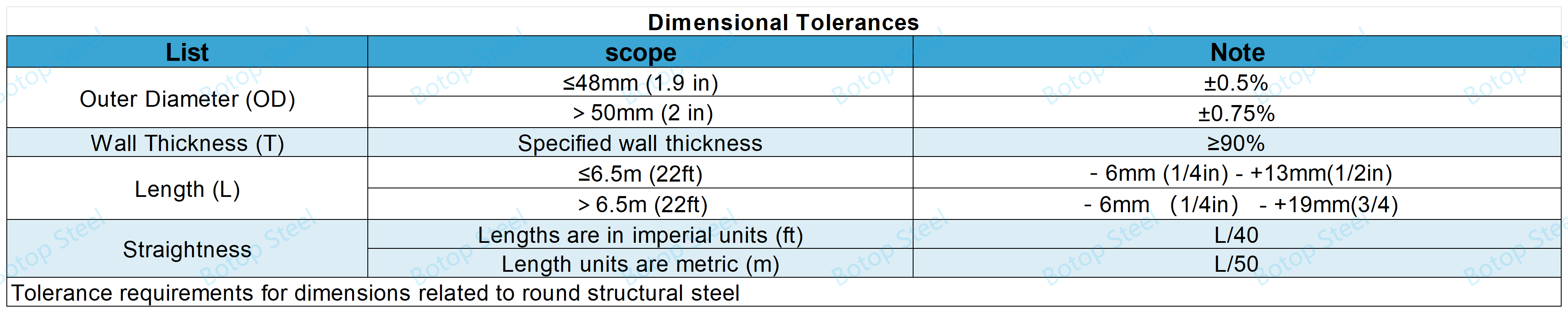
Same Dimensional Tolerance
Example of a round hollow section.
Our Related Products
In choosing whether to use ASTM A500 Grade B or Grade C tubing, the actual engineering requirements and cost-effectiveness need to be considered.
For example, for structures that do not require high strength but good toughness, Grade B may be the more economical choice. For projects that require more strength and load-bearing capacity, Grade C provides the necessary performance, albeit at a higher cost.
Tags: astm a500, grade b, grade c, grade b vs c.
Post time: May-05-2024
